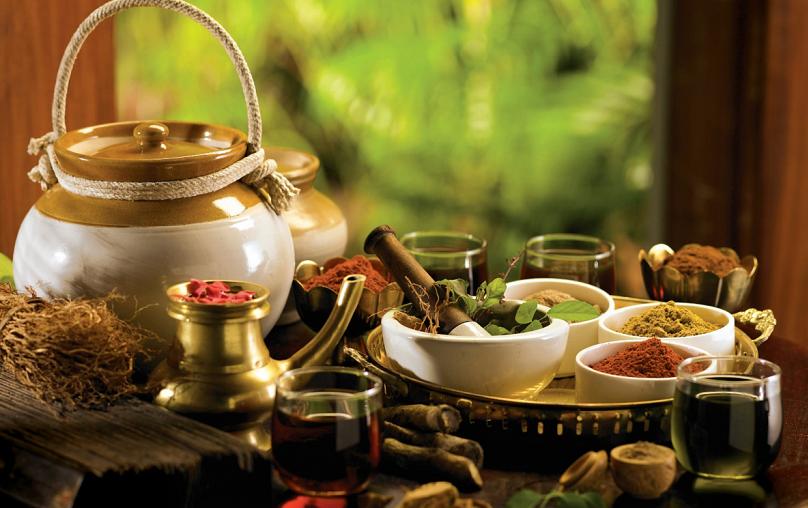
In the vast landscape of healthcare, where options abound and innovations continually emerge, medicine is no longer confined to the rigid boundaries of traditional practices. The evolution of healthcare has given rise to a holistic approach known as Integrative Medicine, where the conventional meets the complementary, and the ancient harmonizes with the modern. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the world of Integrative Medicine, bridging the gap between time-honored traditions and cutting-edge modern approaches.
Understanding Integrative Medicine
Integrative Medicine is a patient-centered approach that combines conventional medicine with complementary therapies to promote overall health and well-being. It emphasizes the importance of the mind-body connection and recognizes that health is influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
At the core of Integrative Medicine is the belief that treatment should not merely alleviate symptoms but address the root causes of illness. It values the partnership between patient and practitioner, aiming to empower individuals to take an active role in their health.
The Key Principles of Integrative Medicine
Integrative Medicine is guided by several fundamental principles:
1. Personalized Care:
Each individual is unique, and their healthcare should reflect this. Integrative Medicine tailors treatments to the patient’s specific needs, considering their physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects.
2. Holistic Approach:
Health is viewed as a combination of physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual well-being. An integrative practitioner considers all these facets when developing a treatment plan.
3. Use of Evidence-Based Therapies:
While integrating complementary therapies, Integrative Medicine relies on scientific evidence to ensure the safety and efficacy of treatments.
4. Prevention and Lifestyle:
Preventive care and lifestyle modifications are essential components of Integrative Medicine. Emphasis is placed on promoting healthy habits to prevent illness.
Common Modalities in Integrative Medicine
Integrative Medicine incorporates a wide range of therapies and approaches, both ancient and modern. Some of the most common modalities include:
1. Acupuncture:
An ancient Chinese practice involving the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
2. Herbal Medicine:
The use of plant-based remedies, such as herbs and botanicals, to treat various health conditions.
3. Mind-Body Practices:
These include meditation, yoga, and tai chi, which promote relaxation and stress reduction.
4. Nutrition and Diet Therapy:
Guidance on dietary choices to support overall health and manage specific conditions.
5. Chiropractic Care:
Manipulation of the spine and musculoskeletal system to improve health and alleviate pain.
6. Massage Therapy:
Hands-on techniques to manipulate muscles and soft tissues for relaxation and pain relief.
7. Functional Medicine:
A systems-oriented approach that addresses the underlying causes of disease, often involving extensive testing and personalized treatment plans.
8. Energy Therapies:
Approaches like Reiki and therapeutic touch that aim to balance the body’s energy flow for healing.
9. Integrative Oncology:
Integrating complementary therapies with conventional cancer treatments to improve overall well-being and reduce side effects.
Benefits of Integrative Medicine
The appeal of Integrative Medicine lies in its ability to offer a more comprehensive and patient-focused approach to healthcare. Some of its key benefits include:
- Holistic Care: Patients are treated as whole individuals, addressing not just symptoms but their overall well-being.
- Reduced Side Effects: Complementary therapies can help manage the side effects of conventional treatments.
- Preventive Focus: The emphasis on lifestyle and prevention can lead to better long-term health outcomes.
- Patient Empowerment: Patients are encouraged to take an active role in their health, making informed decisions.
- Customized Treatment: Treatment plans are tailored to the individual, considering their unique needs and preferences.
Challenges and Criticisms
While Integrative Medicine has gained recognition and popularity, it is not without its challenges and criticisms. Some concerns include:
- Lack of Regulation: The field of complementary therapies is not as rigorously regulated as conventional medicine, leading to concerns about safety and efficacy.
- Cost: Integrative treatments can be costly, and insurance coverage may be limited.
- Scientific Skepticism: Critics argue that some complementary therapies lack robust scientific evidence.
- Complexity: Integrative treatment plans can be complex and require coordination among various practitioners.
Conclusion: A Synergy of Approaches
Integrative Medicine represents a dynamic shift in the way we approach healthcare. It acknowledges that there is no one-size-fits-all solution and embraces the synergy of different approaches to promote healing and well-being. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, Integrative Medicine stands as a testament to the enduring power of ancient wisdom and the relentless pursuit of modern approaches to improve the lives of patients and the vitality of our communities.